
Weld Neck Flange: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
A weld neck flange is a type of flange designed to be welded to a pipe or fitting, providing a secure and leak-proof connection. Known for its strength and durability, the weld neck flange is widely used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, such as in oil and gas pipelines, chemical processing plants, and power generation facilities.
This guide will cover everything you need to know about weld neck flanges, including their design, types, applications, and advantages. We will also provide detailed tables to help you understand the specifications and selection criteria for weld neck flanges.
What is a Weld Neck Flange?
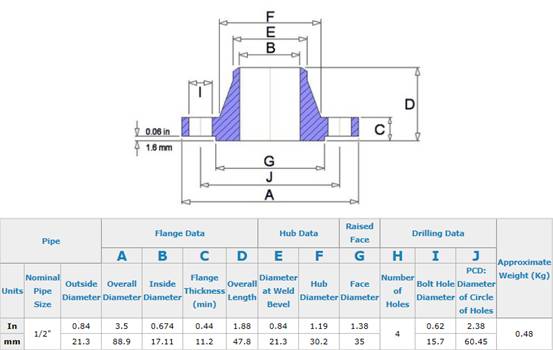
A weld neck flange is a type of flange that has a long, tapered hub that is welded to a pipe. The flange is designed to transfer stress to the pipe, reducing the concentration of stress at the base of the flange. This makes weld neck flanges ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications where the integrity of the connection is critical.
Key Features of Weld Neck Flanges

- Tapered Hub: The long, tapered hub provides reinforcement to the flange and helps distribute stress evenly across the pipe.
- Butt-Welded Connection: The flange is welded to the pipe using a butt-weld, ensuring a strong and leak-proof connection.
- High Strength: Weld neck flanges are known for their strength and durability, making them suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Leak-Proof: The welded connection ensures that the flange is leak-proof, even in high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
Types of Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges come in various types, each designed for specific applications and pressure ratings. Below is a table summarizing the most common types of weld neck flanges.
| Type of Weld Neck Flange | Description | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Weld Neck Flange | The most common type of weld neck flange, used in general piping applications. | Oil and gas pipelines, chemical processing plants. |
| Long Weld Neck Flange | Features an extended neck, used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. | Power generation, high-pressure steam lines. |
| Reducing Weld Neck Flange | Designed to connect pipes of different diameters. | Applications where pipe size transitions are required. |
| Heavy-Duty Weld Neck Flange | Designed for extremely high-pressure applications. | Offshore oil rigs, high-pressure chemical processing. |
Standard Weld Neck Flange

Carbon Steel Forged Weld Neck Flange
The standard weld neck flange is the most commonly used type of weld neck flange. It is designed for general piping applications and is suitable for use in a wide range of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment.
Long Weld Neck Flange
The long weld neck flange features an extended neck, which provides additional reinforcement and is designed for use in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. These flanges are commonly used in power generation plants, high-pressure steam lines, and other applications where the integrity of the connection is critical.
Reducing Weld Neck Flange
A reducing weld neck flange is designed to connect pipes of different diameters. This type of flange is commonly used in applications where a transition from one pipe size to another is required.
Heavy-Duty Weld Neck Flange
The heavy-duty weld neck flange is designed for extremely high-pressure applications, such as offshore oil rigs and high-pressure chemical processing plants. These flanges are made from high-strength materials and are designed to withstand extreme pressure and temperature conditions.
Materials Used for Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges are typically made from a variety of materials, depending on the application and the environmental conditions. Below is a table summarizing the most common materials used for weld neck flanges.
| Material | Corrosion Resistance | Strength | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Moderate | High | General piping, oil and gas pipelines. |
| Stainless Steel | Excellent | High | Chemical processing, corrosive environments. |
| Alloy Steel | Very Good | Very High | High-pressure and high-temperature applications. |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | Excellent | Very High | Offshore oil rigs, chemical processing. |
| Nickel Alloys | Outstanding | Very High | Extreme temperature and corrosive environments. |
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is the most commonly used material for weld neck flanges. It offers high strength and is suitable for general piping applications, such as in oil and gas pipelines. However, carbon steel is not as corrosion-resistant as other materials, so it may not be suitable for corrosive environments.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel weld neck flanges offer excellent corrosion resistance and are commonly used in chemical processing plants, water treatment facilities, and other corrosive environments. Stainless steel is also suitable for high-temperature applications.
Alloy Steel
Alloy steel weld neck flanges are designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. These flanges are made from a combination of metals that provide superior strength and durability, making them ideal for use in power generation plants and high-pressure steam lines.
Duplex Stainless Steel
Duplex stainless steel weld neck flanges offer a combination of high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. These flanges are commonly used in offshore oil rigs, chemical processing plants, and other applications where both strength and corrosion resistance are critical.
Nickel Alloys
Nickel alloy weld neck flanges are designed for extreme temperature and corrosive environments. These flanges are commonly used in applications such as chemical processing, power generation, and offshore oil rigs, where the flange will be exposed to harsh chemicals and high temperatures.
Weld Neck Flange Dimensions and Specifications
Weld neck flanges are available in a wide range of sizes and pressure ratings, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Below is a table summarizing the standard dimensions and pressure ratings for weld neck flanges.
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Outside Diameter (OD) | Bolt Circle Diameter (BCD) | Number of Bolts | Pressure Rating (Class) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 inch | 3.5 inches | 2.38 inches | 4 | 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, 2500 |
| 1 inch | 4.25 inches | 3.12 inches | 4 | 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, 2500 |
| 2 inch | 6 inches | 4.75 inches | 4 | 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, 2500 |
| 4 inch | 9 inches | 7.5 inches | 8 | 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, 2500 |
| 6 inch | 11 inches | 9.5 inches | 8 | 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, 2500 |
| 8 inch | 13.5 inches | 11.75 inches | 8 | 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, 2500 |
Pressure Ratings
Weld neck flanges are available in various pressure ratings, also known as flange classes. The pressure rating of a flange indicates the maximum pressure it can withstand at a given temperature. The most common pressure ratings for weld neck flanges are Class 150, Class 300, Class 600, Class 900, Class 1500, and Class 2500.
- Class 150: Suitable for low-pressure applications.
- Class 300: Suitable for moderate-pressure applications.
- Class 600: Suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Class 900: Suitable for very high-pressure applications.
- Class 1500: Suitable for extremely high-pressure applications.
- Class 2500: Suitable for the highest-pressure applications.
Our Supply Range
Material: Carbon, Alloy and Stainless Steel
Standards: ASTM A105, ASTM A182
Sizes: 1/2” to 24”, Customized up to 48”
Thickness: Schedule 10(S) to SCH 160
Pressure Ratings: Class 150 to 2500
Face Type: RF, RTJ
| Product Name | Carbon Steel Forged Weld Neck Flange |
| Type | Weld Neck Flange, Socket Weld Flange, Slip On Flange, Blind Flange, Thread Flange, Lap Joint Flange, Plate Flange, Reducing Flange, etc. |
| Size | 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, 1 1/4″, 1 1/2″, 2″, 2 1/2″, 3″, 3 1/2″, 4″, 5″, 6″, 8″, 10″, 12″, 14″, 16″, 18″, 20″, 22″, 24″, 26″, 28″, 30″, 32″, 34″, 36″, 38″, 40″, 42″, 44″, 46″, 48″ |
| DN15, DN20, DN25, DN32, DN40, DN50, DN65, DN80, DN90, DN100, DN125, DN150, DN200, DN250, DN300, DN350, DN400, DN450, DN500, DN550, DN600, DN650, DN700, DN750, DN800, DN850, DN900, DN950, DN1000, DN1050, DN1100, DN1150, DN1200 | |
| Material | Carbon Steel |
| Grade | A105, RST37.2, C22.8, Q235, etc. |
| Pressure | PN6, PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, etc. |
| Wall Thickness | Sch10, Sch20, Sch30, STD, Sch40, Sch60, XS, Sch80, Sch100, Sch120, Sch140, Sch160, XXS, etc. |
| Standard | ANSI/ASME B16.5, ANSI/ASME B16.47, DIN, JIS, GOST, UNI, etc. |
Two Shapes of Welding Neck Flange
Welding neck flange have two forms (shapes), one with reducing neck as we called reducing weld neck flange; One with a even diameter of typical long neck named as long neck weld flange.
Reducing Weld Neck Flange

As it’s name it is like a combination of pipe reducer and flange, so it could be welded to a smaller pipe directly.
Long Weld Neck Flange
Simplified called as LWN flange, the neck part seems like a elongated pipe and connected to a flange. So in most cases it works as a nozzle for a column or a barrel.

You can choose for a normal thickness long welding neck flange or a heavy LWN flange that with bigger thickness and a differently shape.
Face Type
Like other flanges it has Raised Face (RF) Type and Ring Type Joint (RTJ).
Raised Face Weld Neck Flange
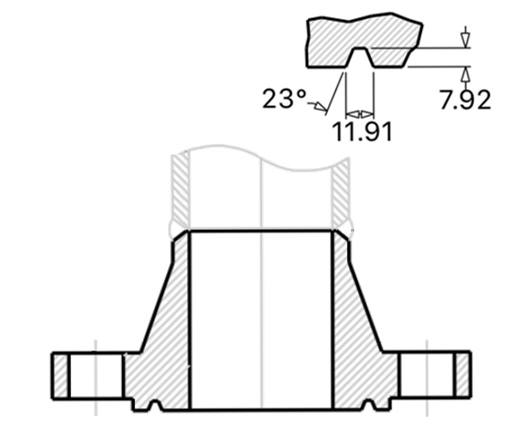
RTJ Weld Neck Flange
Raised face weld neck flange bottom side has a small portion surrounding the bore that protrudes from the face. Gasket seat will be placed in this raised area. Depending on the different pressure ratings, different height of raised face will be adopted. For example, 150# and 300# flange raised face height is 1/6”, above 300# the height will be above 1/4”.
The ring-joint type of WN flange has a special made groove, here you can place a metal gasket seat to seal the connects. So this type of SW flange is used in high temperature and high pressure services.
Bolt Patterns
The bolt pattern of a weld neck flange refers to the number and size of bolts required to secure the flange to the pipe or fitting. The bolt pattern is determined by the size and pressure rating of the flange. For example, a 4-inch weld neck flange with a Class 150 pressure rating will typically require 8 bolts, while a 6-inch weld neck flange with a Class 300 pressure rating will require 12 bolts.
Applications of Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges are used in a wide range of industries and applications due to their strength, durability, and leak-proof design. Below are some of the most common uses of weld neck flanges.
1. Oil and Gas Pipelines
Weld neck flanges are commonly used in oil and gas pipelines to connect pipes and fittings. The high strength and leak-proof design of the weld neck flange make it ideal for use in high-pressure and high-temperature environments, such as in offshore oil rigs and natural gas pipelines.
2. Chemical Processing Plants
In chemical processing plants, weld neck flanges are used to connect pipes that transport corrosive chemicals. Stainless steel and nickel alloy weld neck flanges are commonly used in these applications due to their excellent corrosion resistance.
3. Power Generation
Weld neck flanges are used in power generation plants to connect pipes that transport steam, water, and other fluids. Long weld neck flanges are commonly used in high-pressure steam lines, while alloy steel flanges are used in high-temperature applications.
4. Water Treatment Facilities
In water treatment facilities, weld neck flanges are used to connect pipes that transport water and other fluids. Stainless steel weld neck flanges are commonly used in these applications due to their corrosion resistance and durability.
5. Offshore Oil Rigs
Weld neck flanges are used in offshore oil rigs to connect pipes that transport oil and gas. Duplex stainless steel and nickel alloy weld neck flanges are commonly used in these applications due to their high strength and corrosion resistance.
Advantages of Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges offer several advantages over other types of flanges, making them the preferred choice for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Below are some of the key advantages of using weld neck flanges.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Strength | Weld neck flanges are known for their strength and durability, making them suitable for high-pressure applications. |
| Leak-Proof Connection | The welded connection ensures that the flange is leak-proof, even in high-pressure and high-temperature environments. |
| Stress Distribution | The tapered hub of the weld neck flange helps distribute stress evenly across the pipe, reducing the risk of failure. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Weld neck flanges made from stainless steel or nickel alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance. |
| Versatility | Weld neck flanges are available in a wide range of sizes, materials, and pressure ratings, making them suitable for a variety of applications. |
How to Install a Weld Neck Flange
Installing a weld neck flange requires careful preparation and precision to ensure a secure and leak-proof connection. Below are the general steps for installing a weld neck flange.
Step 1: Prepare the Pipe
- Ensure that the pipe is clean and free of debris.
- Cut the pipe to the desired length and bevel the edges to prepare for welding.
Step 2: Align the Flange
- Slide the weld neck flange onto the pipe, ensuring that the flange is properly aligned with the pipe.
- Use alignment tools if necessary to ensure that the flange is centered on the pipe.
Step 3: Weld the Flange
- Use a butt-weld to weld the flange to the pipe.
- Ensure that the weld is smooth and free of defects to prevent leaks.
Step 4: Bolt the Flange
- Once the flange is welded to the pipe, use bolts to secure the flange to the mating flange or fitting.
- Tighten the bolts evenly to ensure a secure connection.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between a weld neck flange and a slip-on flange?
A weld neck flange is welded to the pipe using a butt-weld, while a slip-on flange is slipped over the pipe and welded in place. Weld neck flanges offer higher strength and are suitable for high-pressure applications, while slip-on flanges are easier to install but are not as strong.
2. What is the purpose of the tapered hub on a weld neck flange?
The tapered hub on a weld neck flange helps distribute stress evenly across the pipe, reducing the concentration of stress at the base of the flange. This makes weld neck flanges ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
3. Can weld neck flanges be used in corrosive environments?
Yes, weld neck flanges made from materials such as stainless steel, duplex stainless steel, and nickel alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance and can be used in corrosive environments.
4. What is the maximum pressure rating for a weld neck flange?
Weld neck flanges are available in pressure ratings up to Class 2500, which is suitable for extremely high-pressure applications.
5. How do I choose the right weld neck flange for my application?
When choosing a weld neck flange, consider factors such as the pressure rating, material, size, and corrosion resistance required for your specific application. Consulting with a professional engineer or supplier can help ensure that you select the right flange for your needs.
Weld neck flanges are an essential component in a wide range of industries, from oil and gas pipelines to chemical processing plants. Their strength, durability, and leak-proof design make them the preferred choice for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. By selecting the right weld neck flange for your project and installing it properly, you can ensure a secure and reliable connection that will last for years to come.




You must be logged in to post a comment.